In this 5-10 minute introduction to the Visual Studio integrated development environment (IDE), you'll create a simple Node.js web application. 2 steps closer! puerto rican genealogy.

Visual Studio Code is able to detect that this is a Node.js project, and as a result, automatically downloaded the TypeScript typings file for Node.js from NPM. The typings file allows you to get autocompletion for other Node.js globals, such as Buffer and setTimeout, as well as all of the built-in modules such as fs and http. The solution is to set alias default. In the OS terminal run. Nvm alias default 7.8.0. Open vscode, now running node -v returns 7.8.0. It seems vscode takes up this (alias default) value and not the node version that is set by nvm use X.X.X. Restart VS code for it to pick up the changes. Update - This solution might not work for. Working with MongoDB. Visual Studio Code has great support for working with MongoDB databases, whether your own instance or in Azure with MongoDB Atlas.With the MongoDB for VS Code extension, you can create, manage, and query MongoDB databases from within VS Code. Install the extension. MongoDB support for VS Code is provided by the MongoDB for VS Code extension.

Prerequisites
You must have Visual Studio installed and the Node.js development workload.
If you haven't already installed Visual Studio 2019, go to the Visual Studio downloads page to install it for free.
If you haven't already installed Visual Studio 2017, go to the Visual Studio downloads page to install it for free.
If you need to install the workload but already have Visual Studio, go to Tools > Get Tools and Features.., which opens the Visual Studio Installer. Choose the Node.js development workload, then choose Modify.
You must have the Node.js runtime installed.
If you don't have it installed, we recommend you install the LTS version from the Node.js website for best compatibility with outside frameworks and libraries. Node.js is built for 32-bit and 64-bit architectures. The Node.js tools in Visual Studio, included in the Node.js workload, support both versions. Only one is required and the Node.js installer only supports one being installed at a time.
In general, Visual Studio automatically detects the installed Node.js runtime. If it does not detect an installed runtime, you can configure your project to reference the installed runtime in the properties page (after you create a project, right-click the project node, choose Properties, and set the Node.exe path). You can use a global installation of Node.js or you can specify the path to a local interpreter in each of your Node.js projects.

Create a project
First, you'll create an Node.js web application project.
If you don't have the Node.js runtime already installed, install the LTS version from the Node.js website.
For more information, see the prerequisites.
Open Visual Studio.
Create a new project. Super driftwatermelon gaming.
Press Esc to close the start window. Type Ctrl + Q to open the search box, type Node.js, then choose Create new Blank Node.js Web application project (JavaScript). In the dialog box that appears, choose Create.
From the top menu bar, choose File > New > Project. In the left pane of the New Project dialog box, expand JavaScript, then choose Node.js. In the middle pane, choose Blank Node.js Web application, then choose OK.
If you don't see the Blank Node.js Web application project template, you must add the Node.js development workload. For detailed instructions, see the Prerequisites.
Visual Studio creates and the new solution and opens the project. server.js opens in the editor in the left pane.
Explore the IDE
Take a look at Solution Explorer in the right pane.
Highlighted in bold is your project, using the name you gave in the New Project dialog box. On disk, this project is represented by a .njsproj file in your project folder.
At the top level is a solution, which by default has the same name as your project. A solution, represented by a .sln file on disk, is a container for one or more related projects.
The npm node shows any installed npm packages. You can right-click the npm node to search for and install npm packages using a dialog box.
If you want to install npm packages or Node.js commands from a command prompt, right-click the project node and choose Open Command Prompt Here.
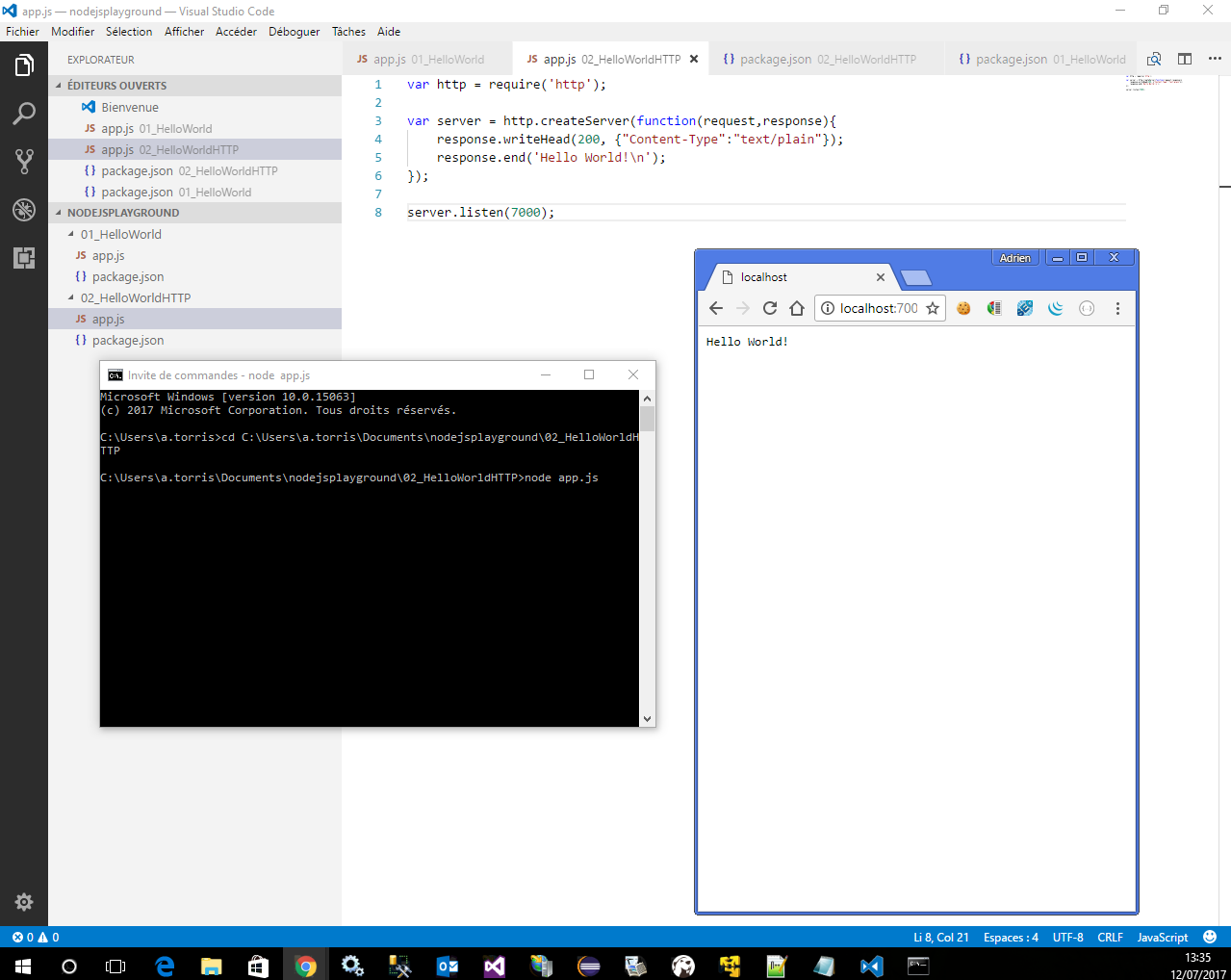
In the server.js file in the editor (left pane), choose
http.createServerand then press F12 or choose Go To Definition from the context (right-click) menu. This command takes you to the definition of thecreateServerfunction in index.d.ts.Got back to server.js, then put your cursor at the end of the string in this line of code,
res.end('Hello Worldn');, and modify it so that it looks like this:res.end('Hello Worldn' + res.connection.Where you type
connection., IntelliSense provides options to auto-complete the code entry.Choose localPort, and then type
);to complete the statement so that it looks like this:res.end('Hello Worldn' + res.connection.localPort);
Run the application
Visual Studio Code Node
Press Ctrl+F5 (or Debug > Start Without Debugging) to run the application. The app opens in a browser.
In the browser window, you will see 'Hello World' plus the local port number.
Close the web browser.
Congratulations on completing this Quickstart in which you got started with the Visual Studio IDE and Node.js. If you'd like to delve deeper into its capabilities, continue with a tutorial in the Tutorials section of the table of contents.

Visual Code Node Js
Next steps
